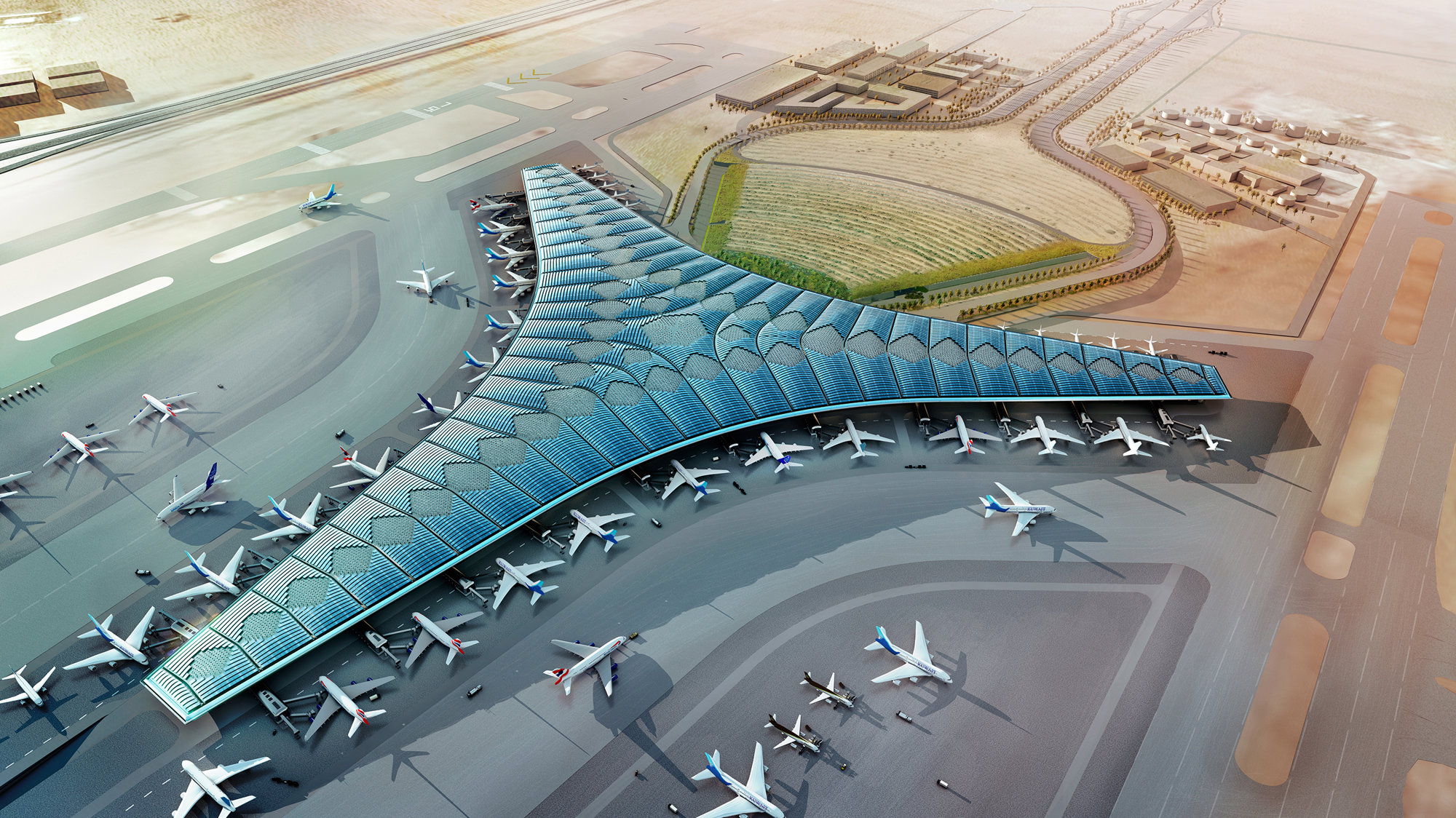
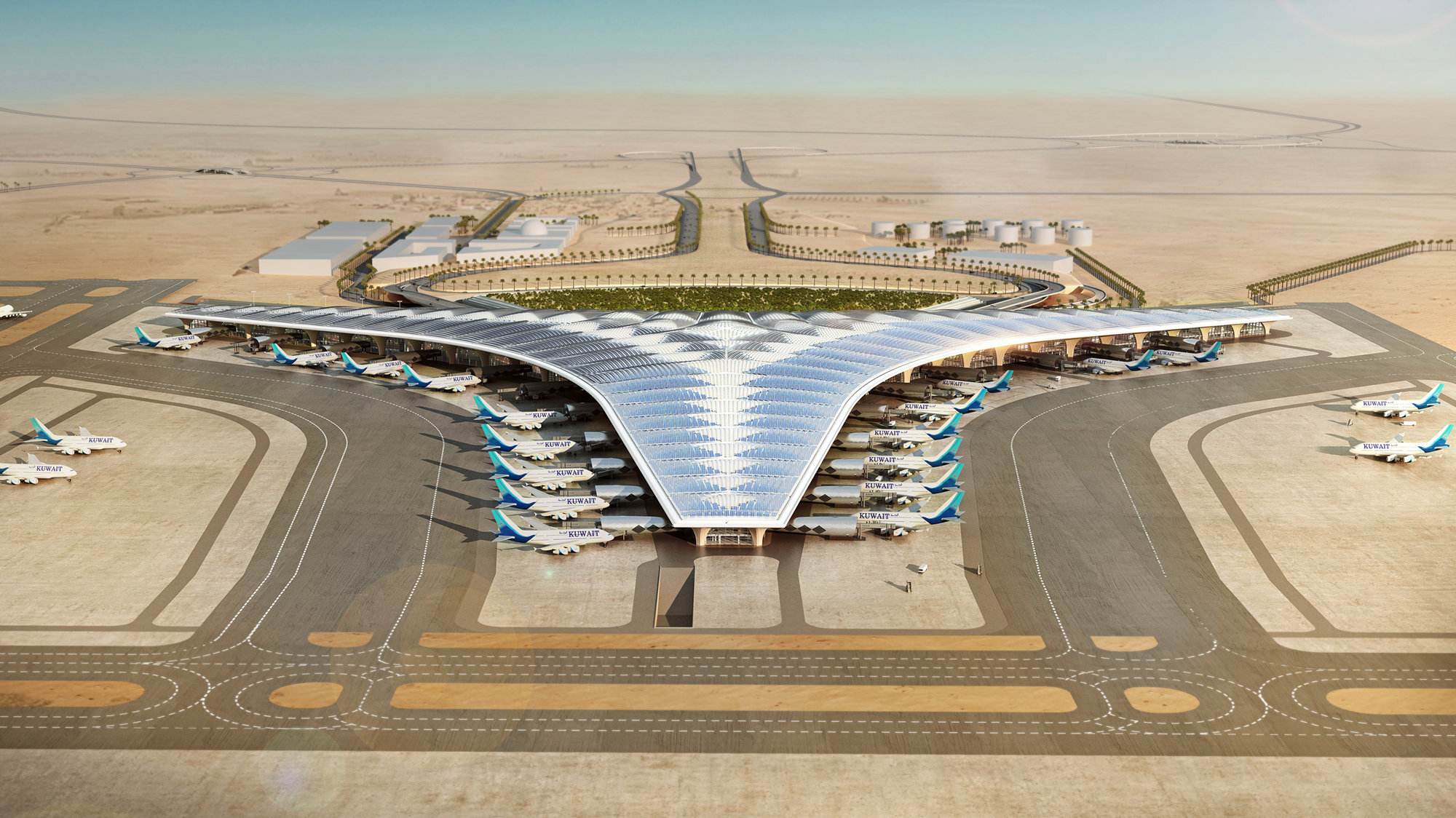
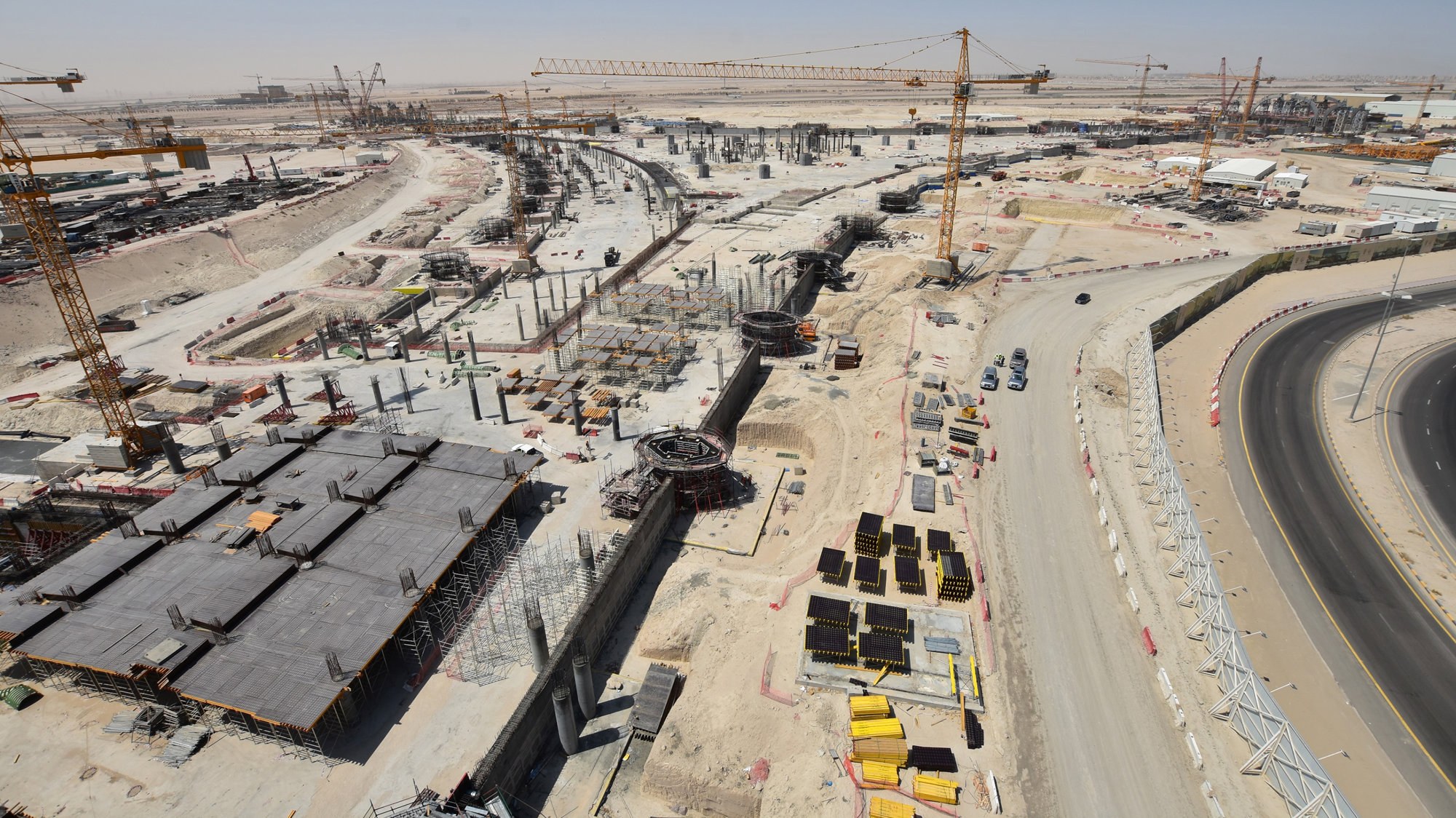
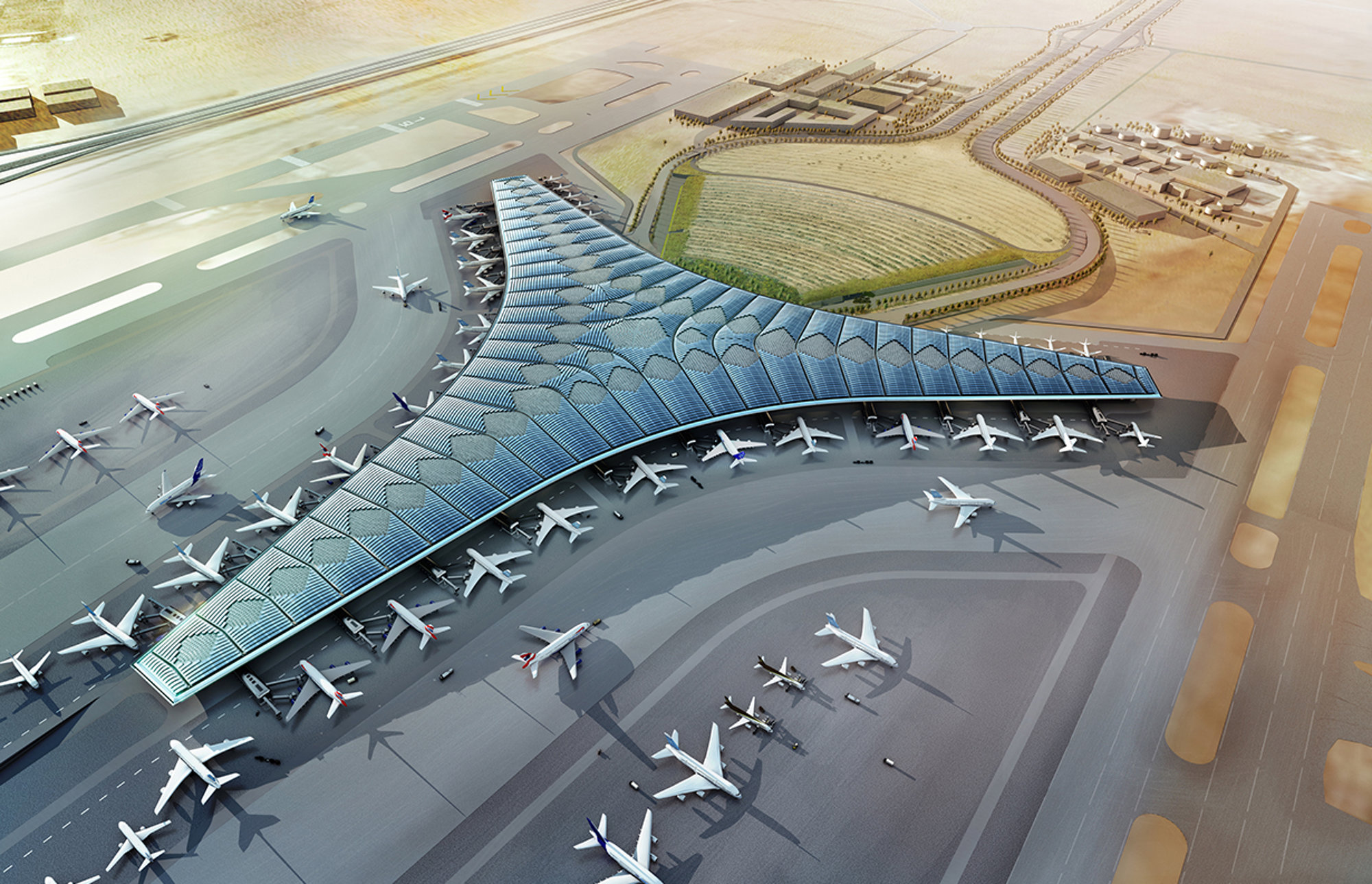
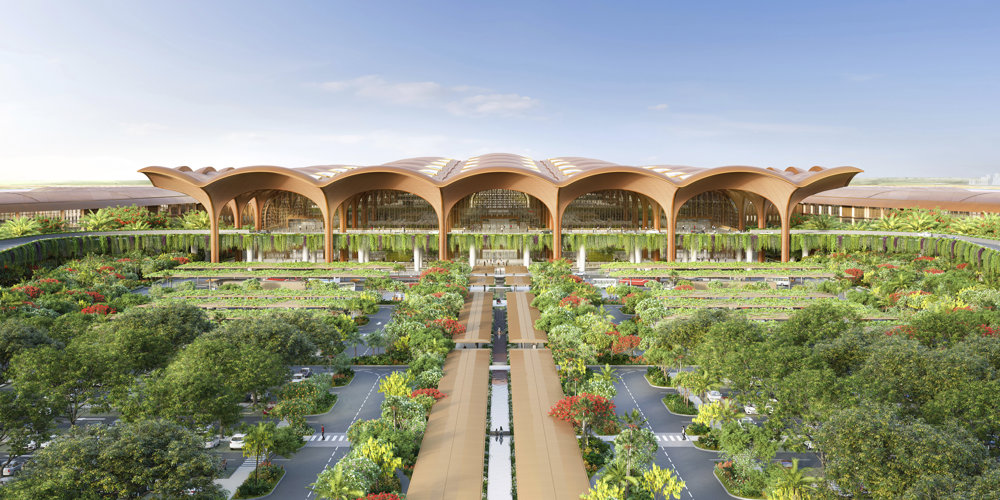
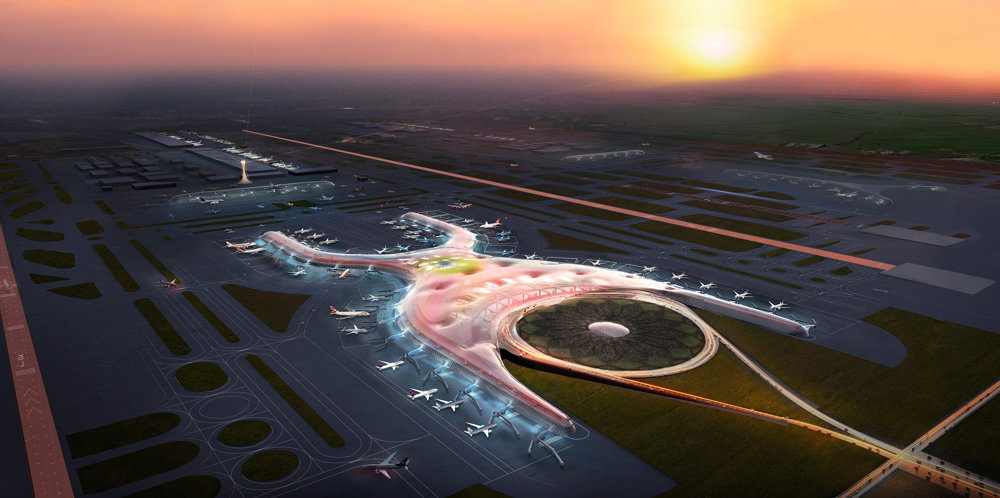
Kuwait International Airport is planned to significantly increase capacity and establish a new regional air hub in the Gulf - these strategic aims will be matched by a state-of-the-art terminal building, which will provide the highest levels of comfort for passengers and will set a new environmental benchmark for airport buildings. Its design is rooted in a sense of place, responsive to the climate of one of the hottest inhabited environments on earth and inspired by local forms and materials.
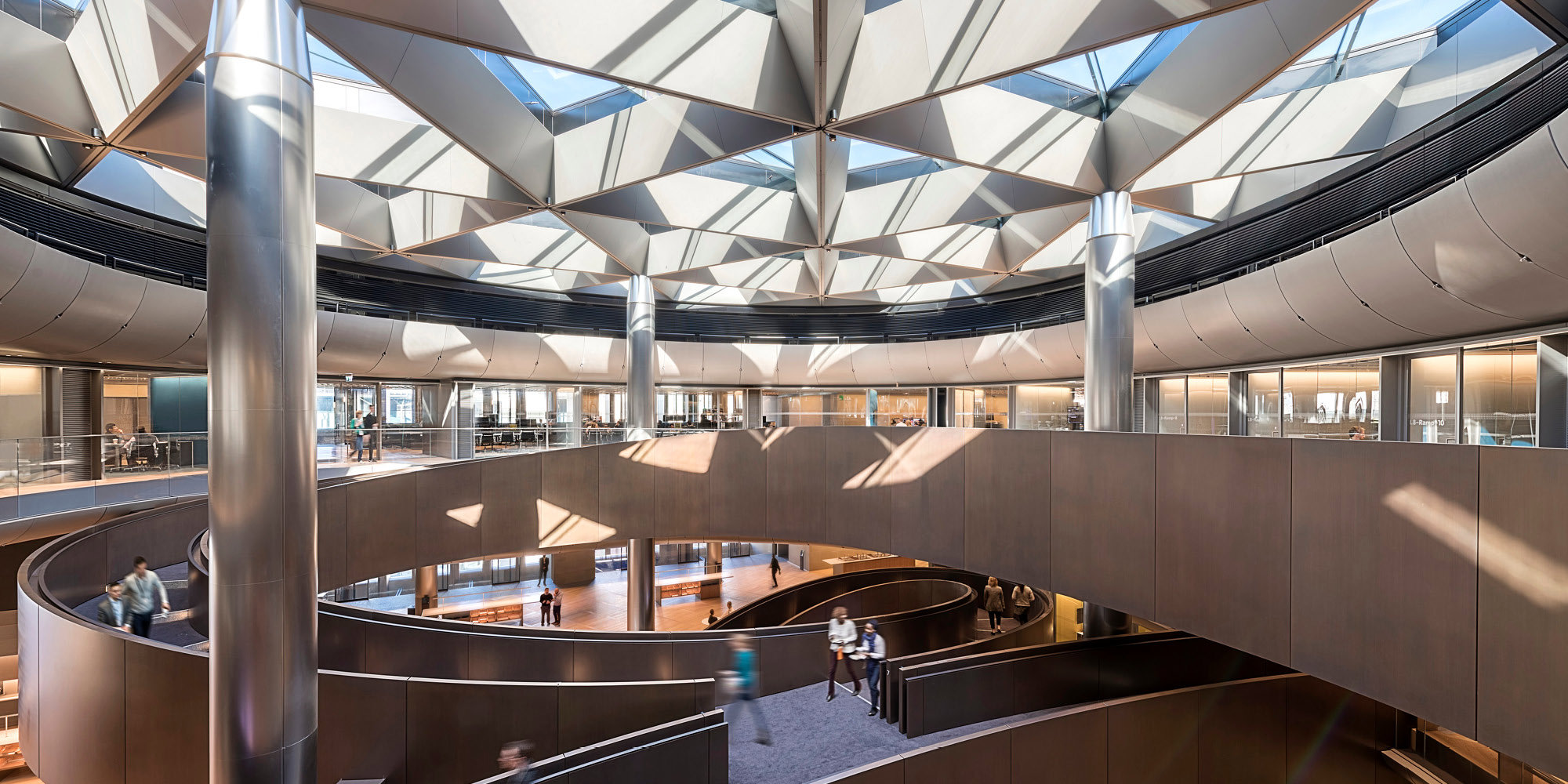
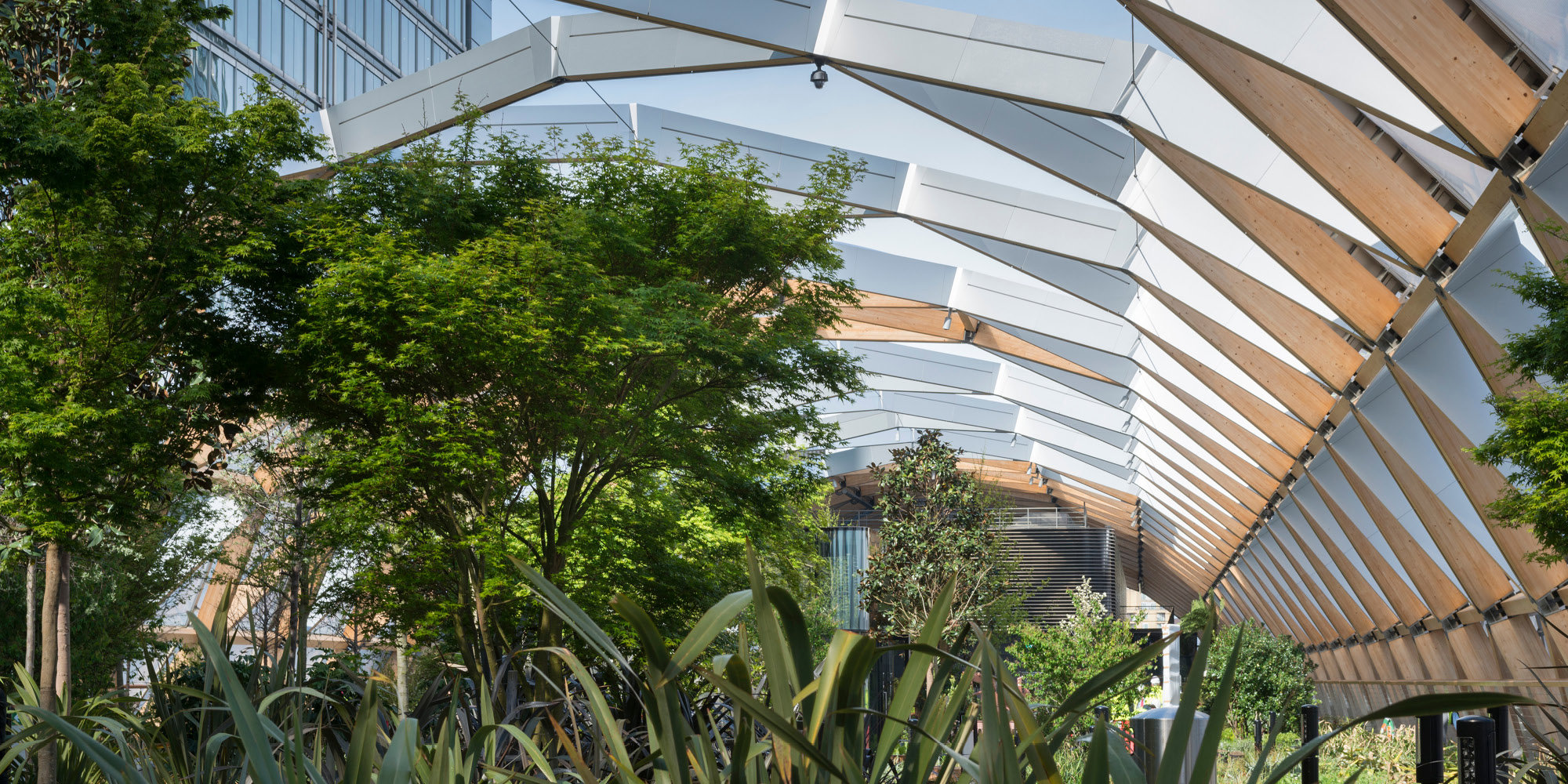
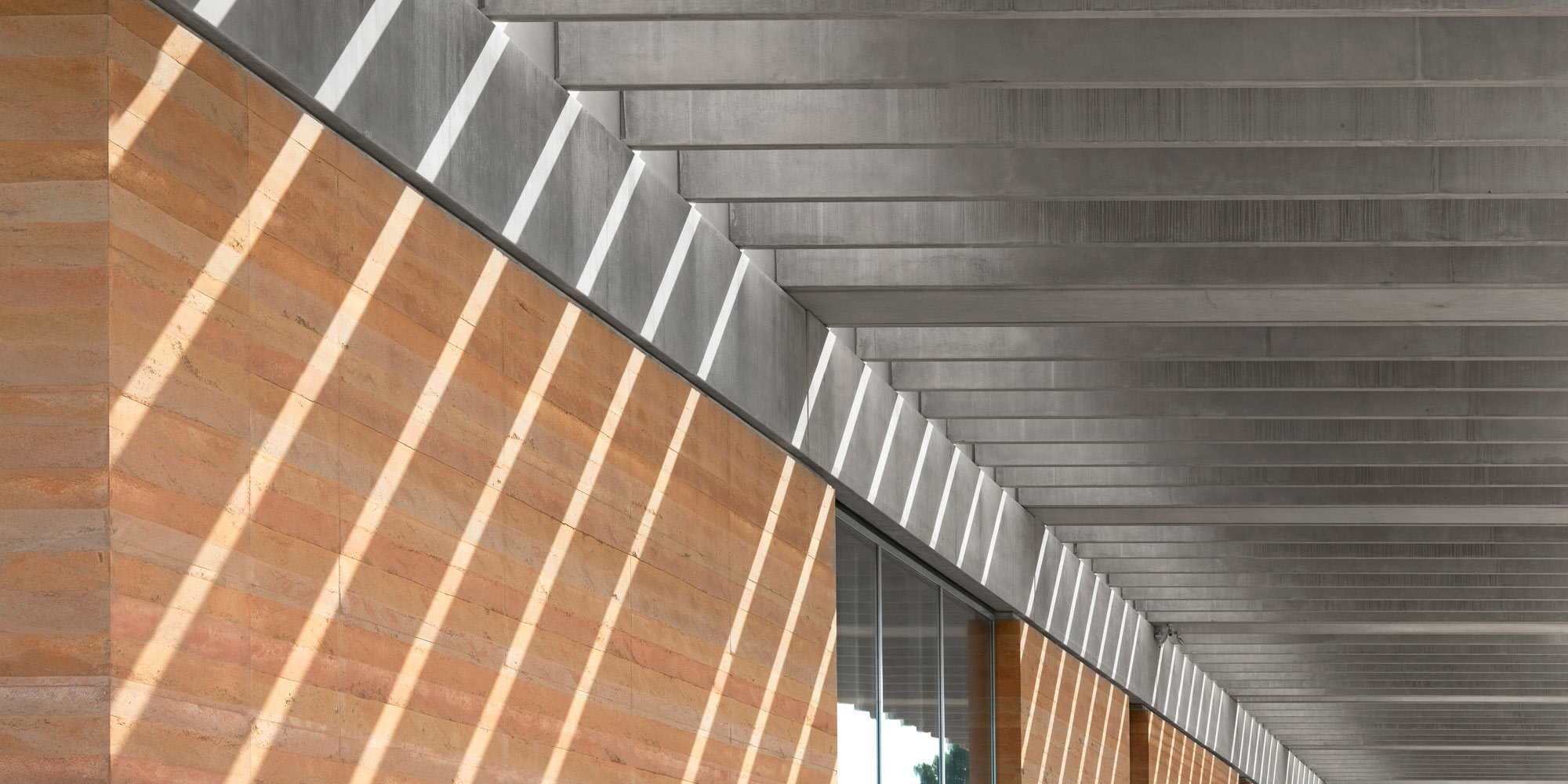
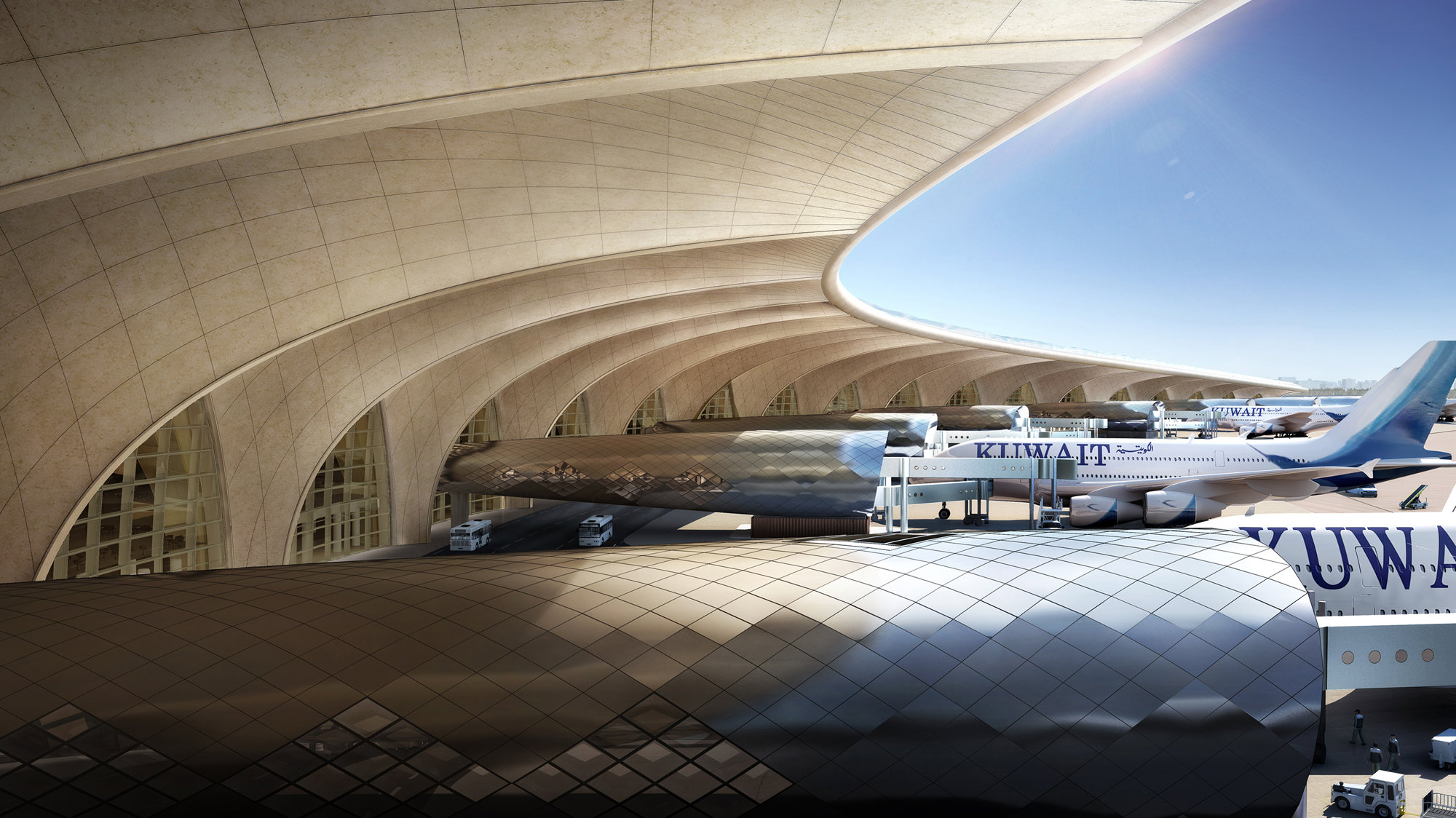
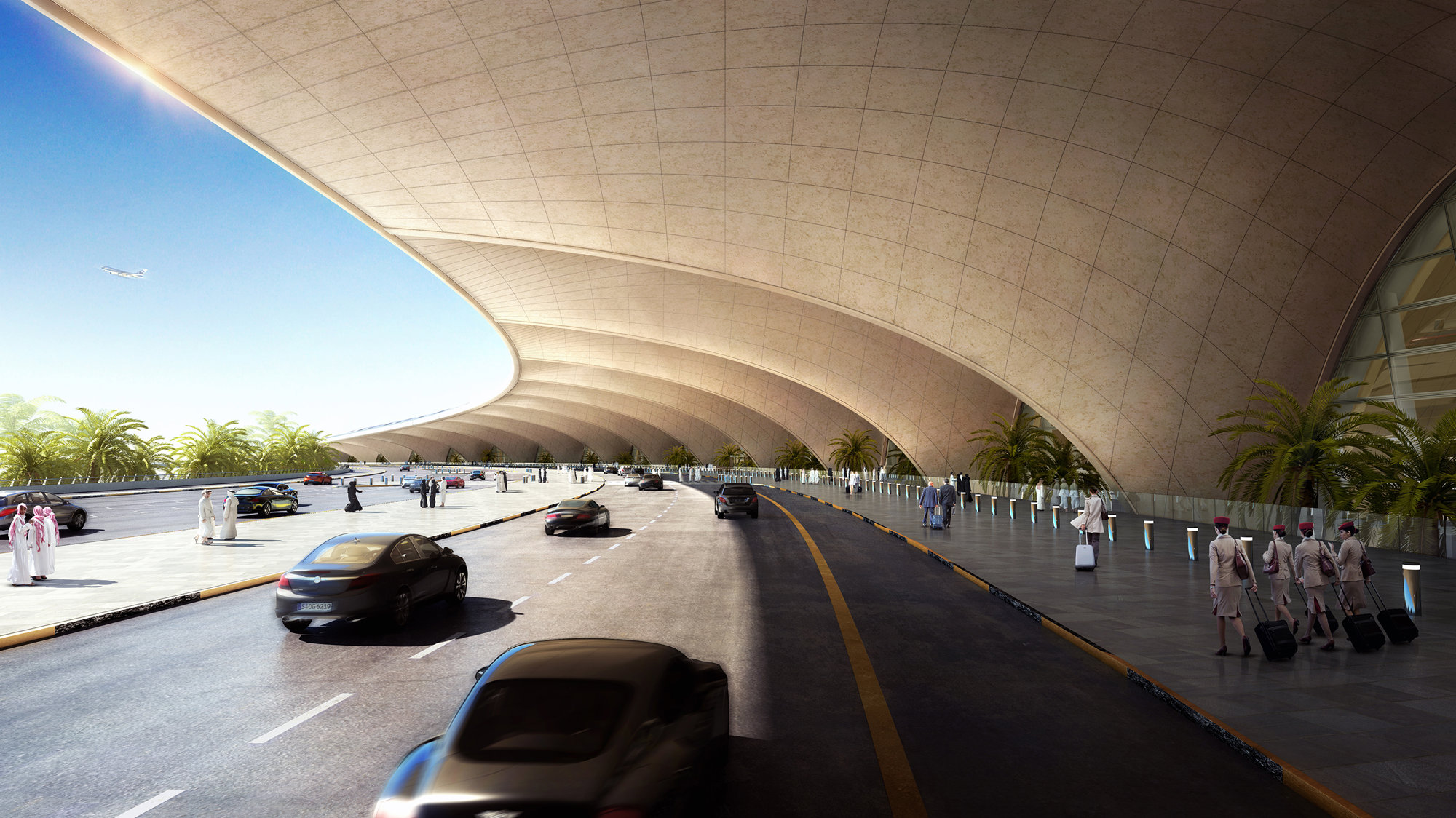
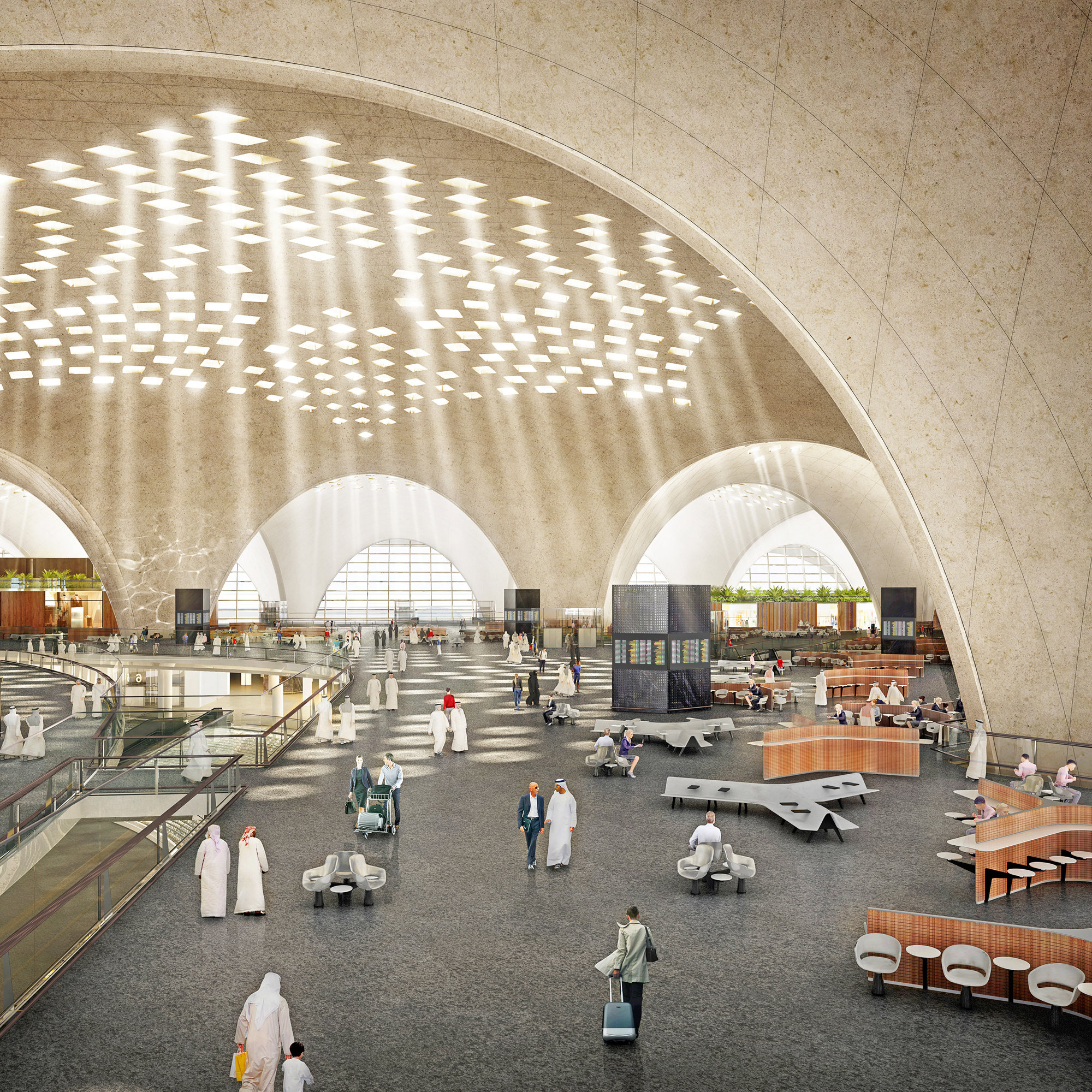
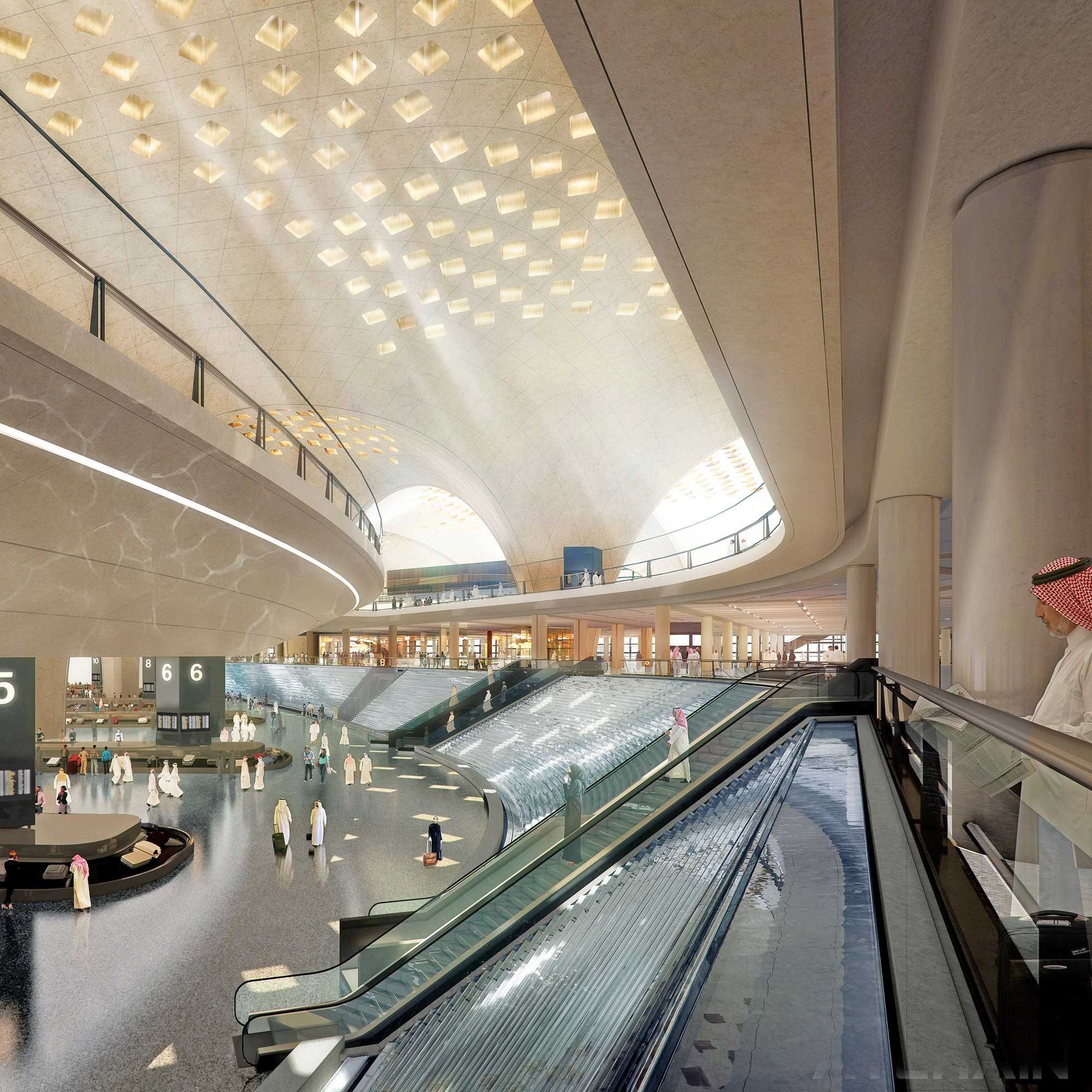
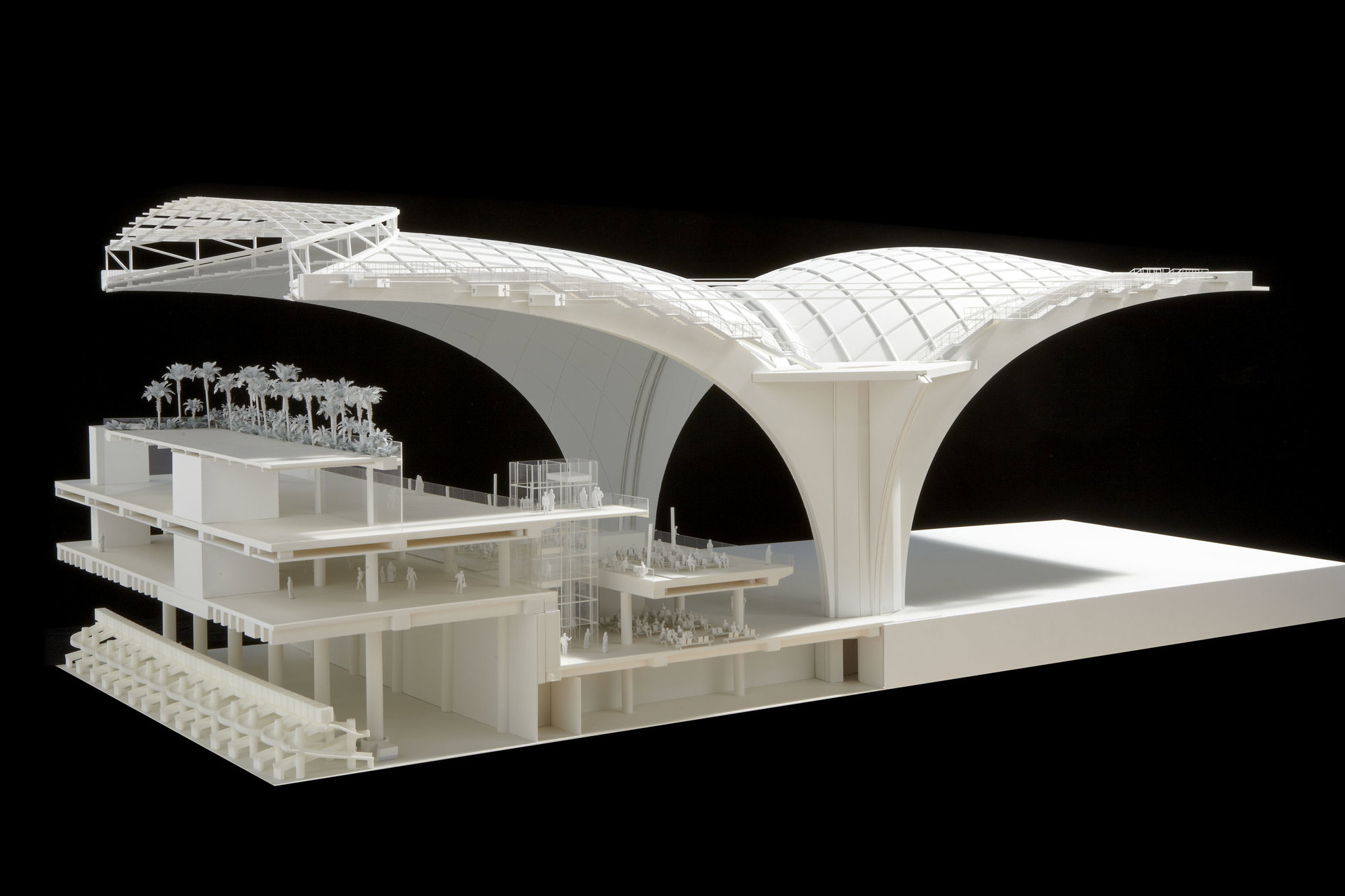
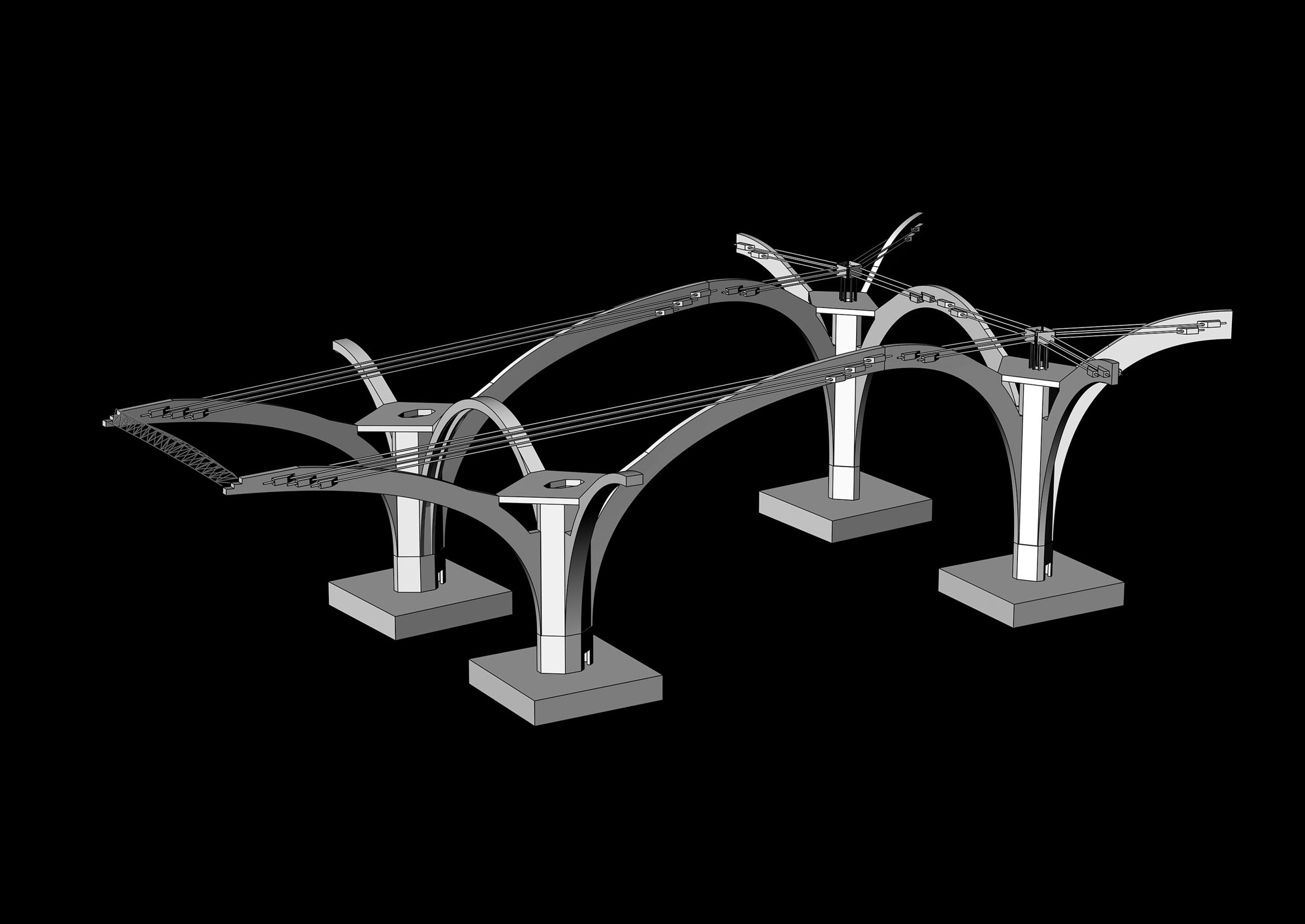
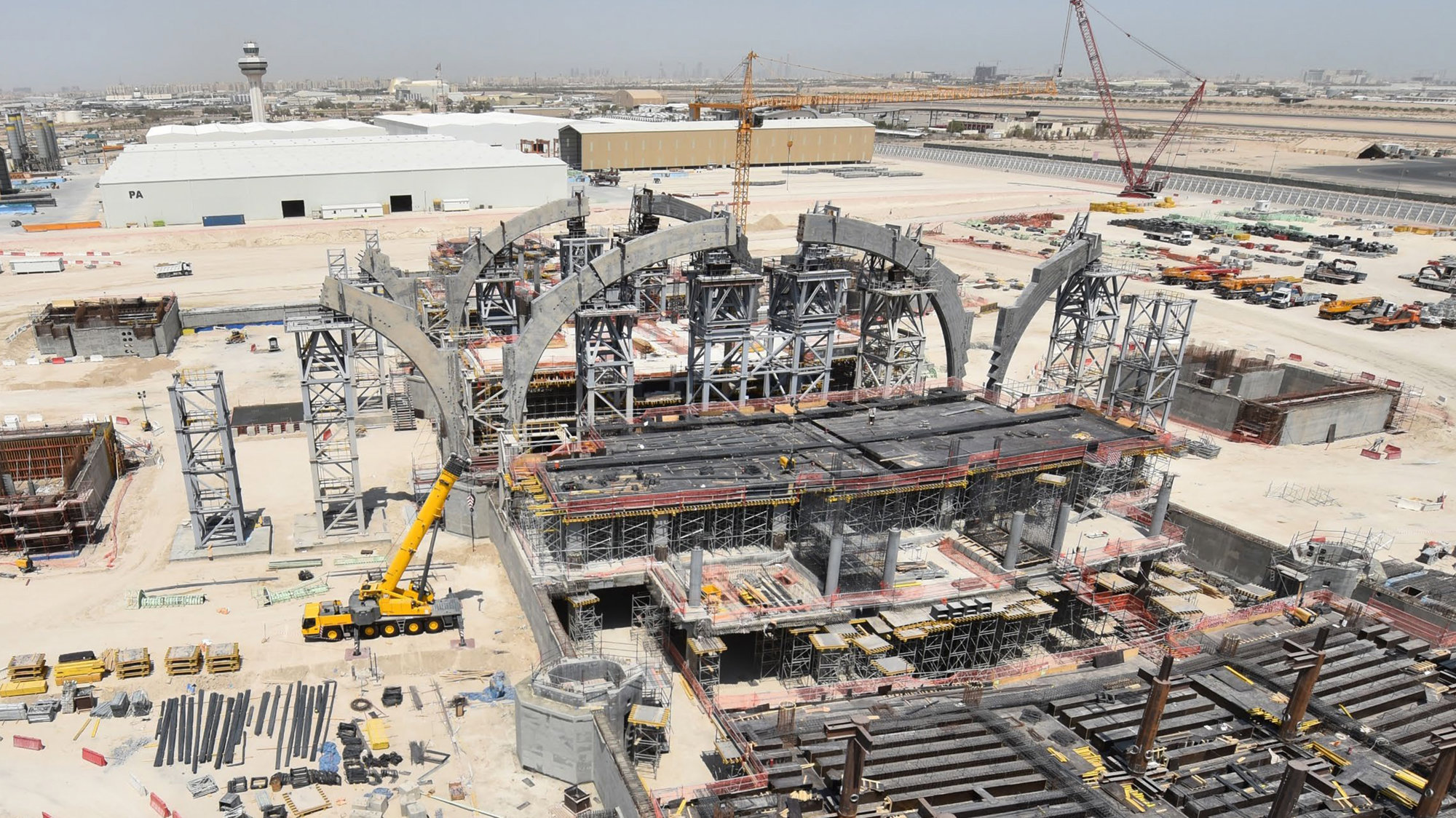
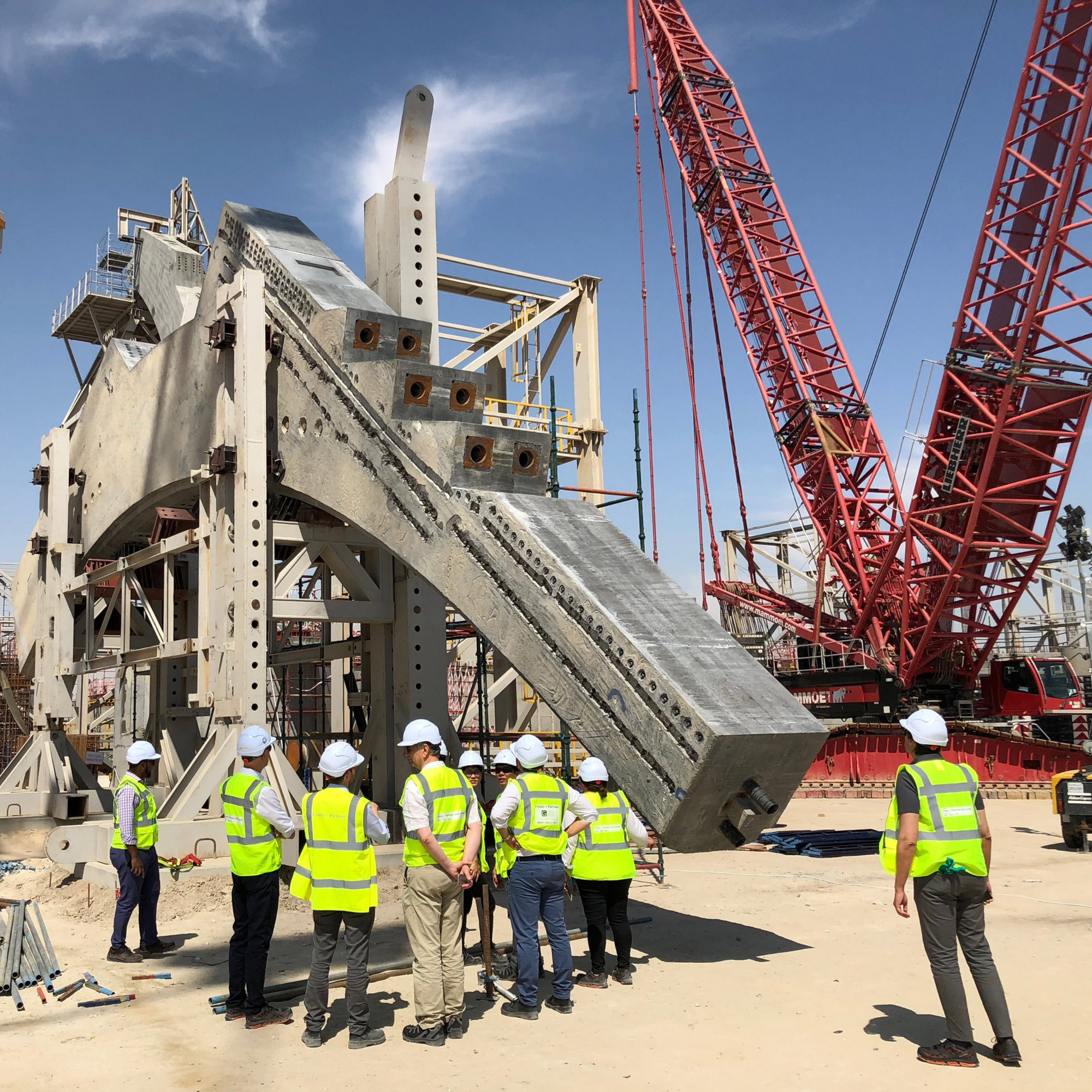
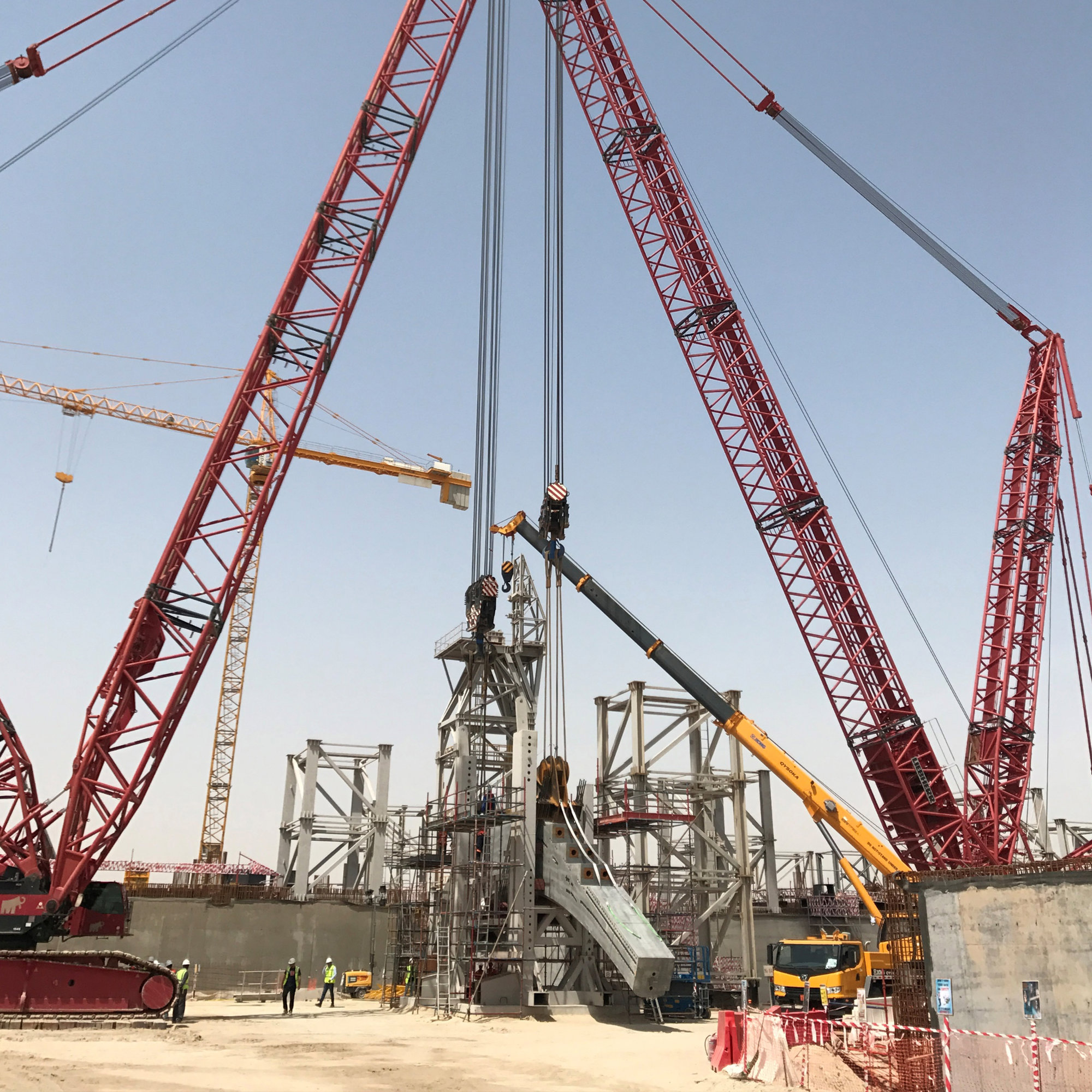
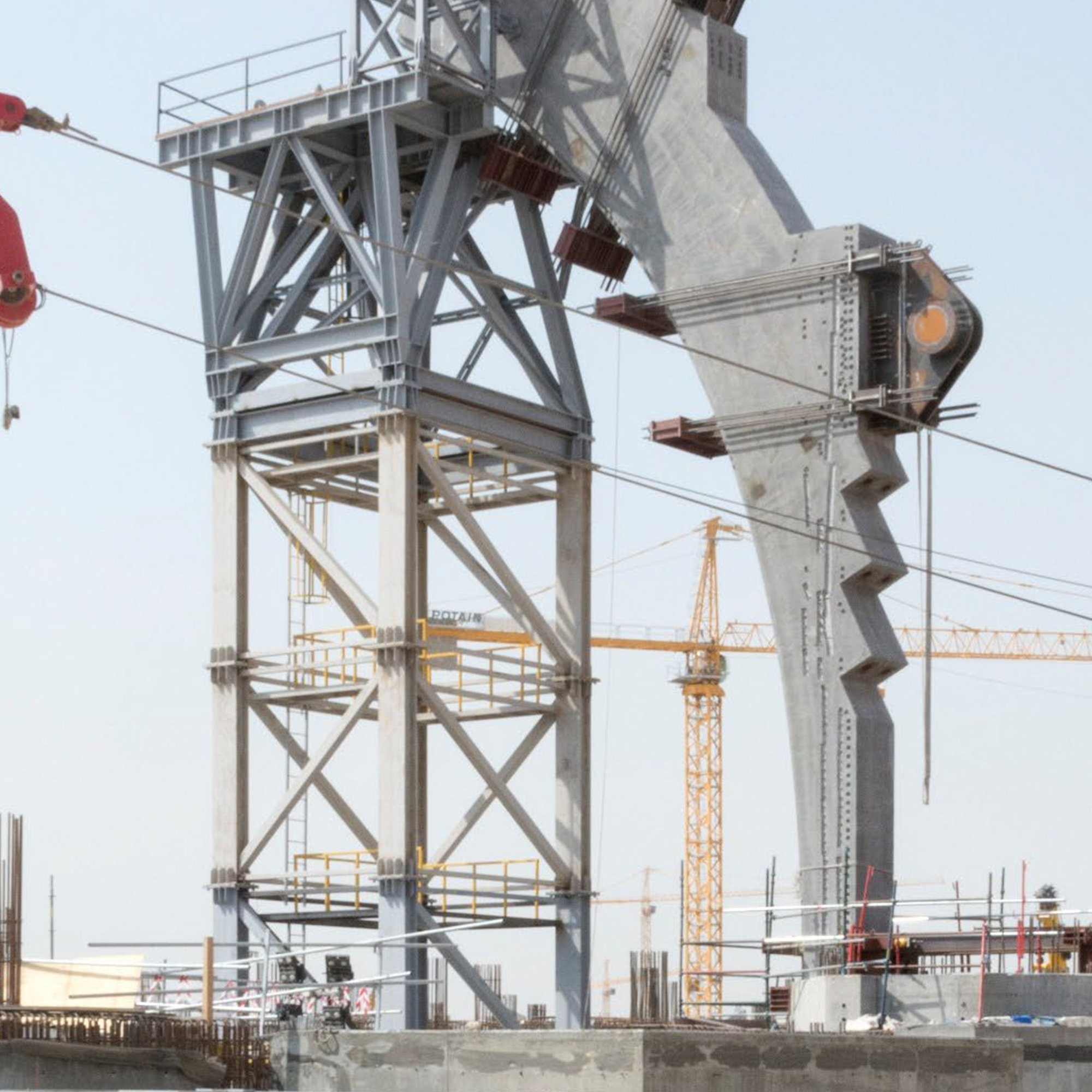
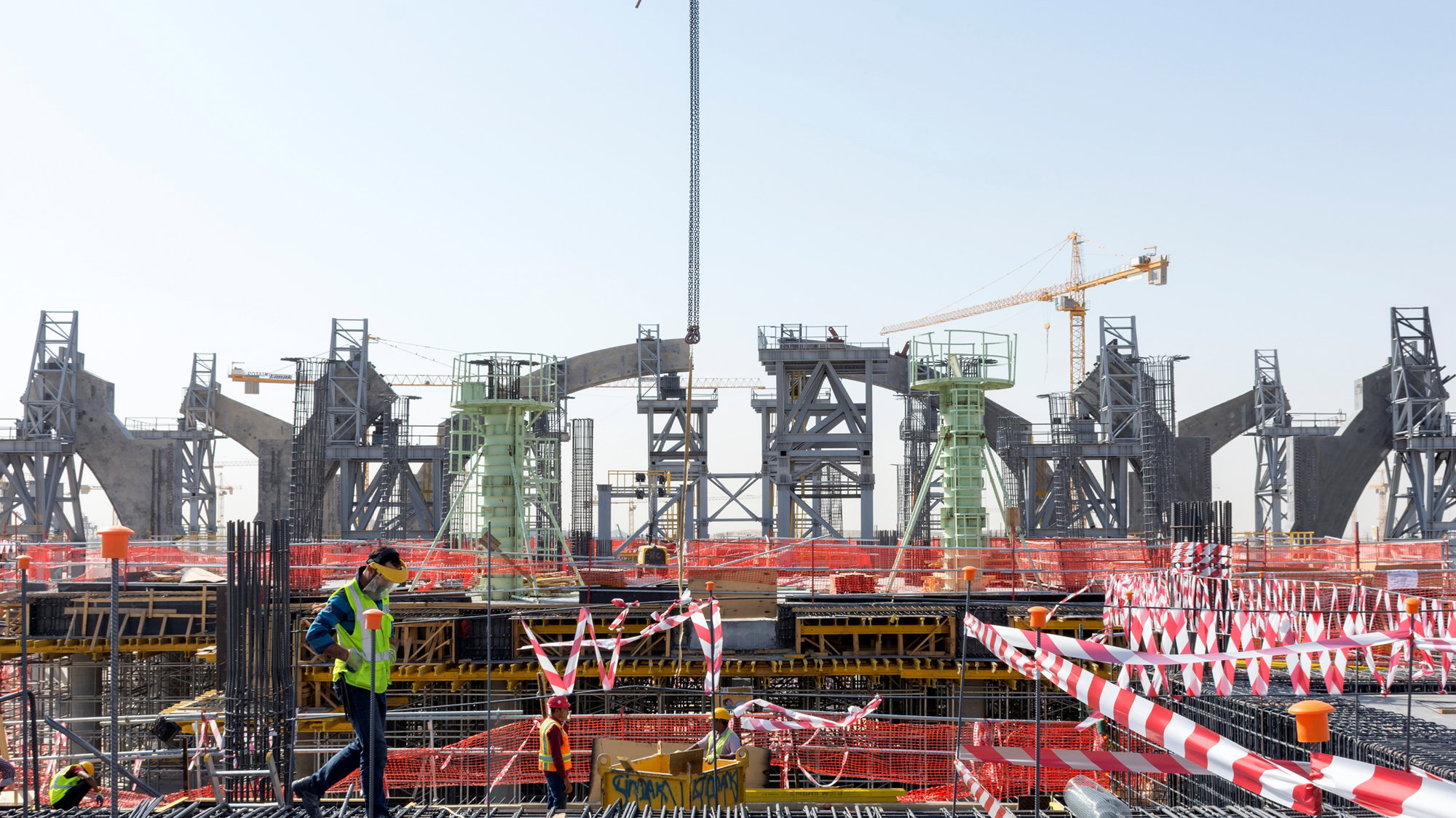
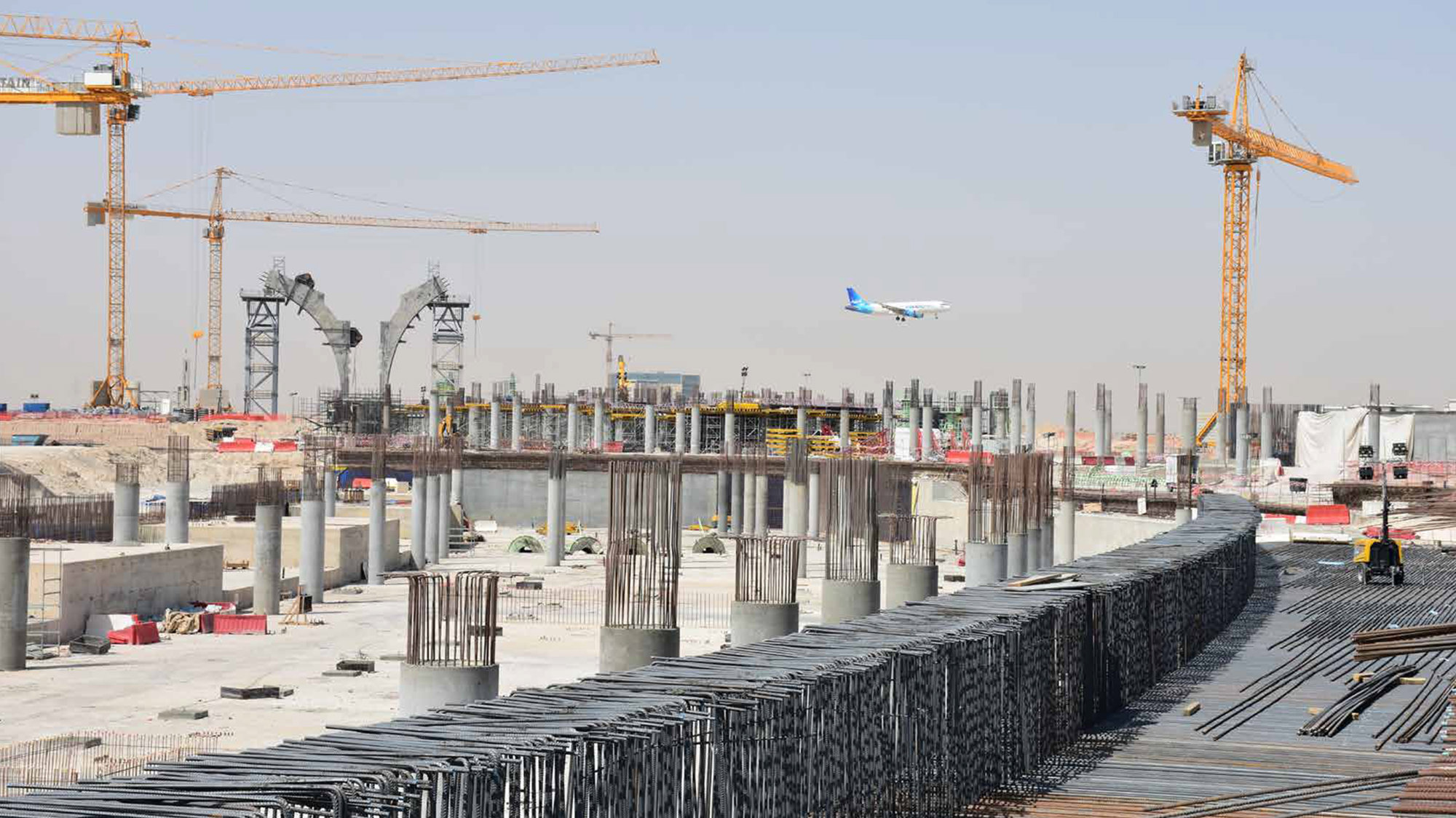
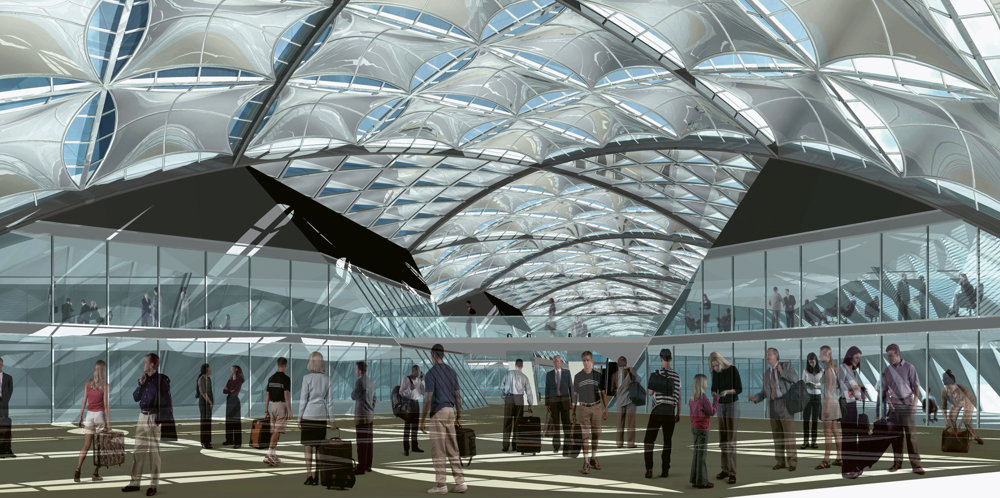
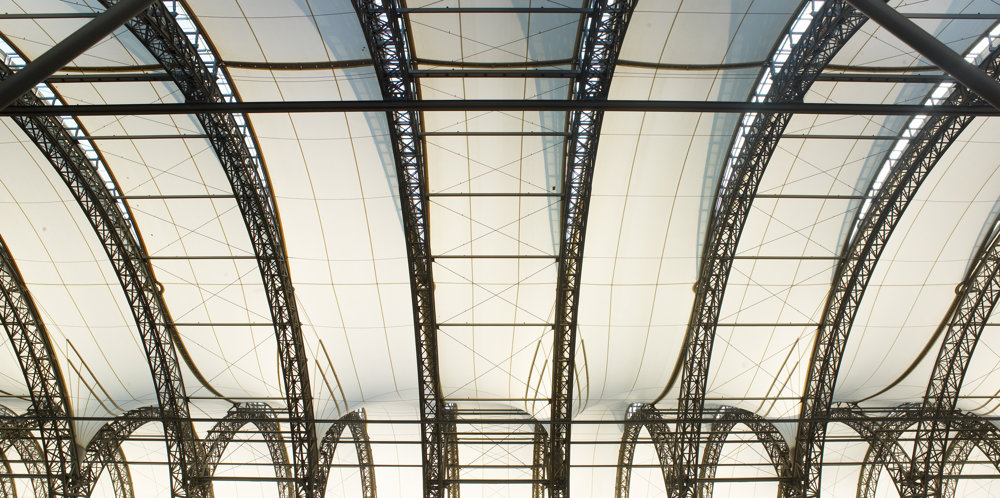
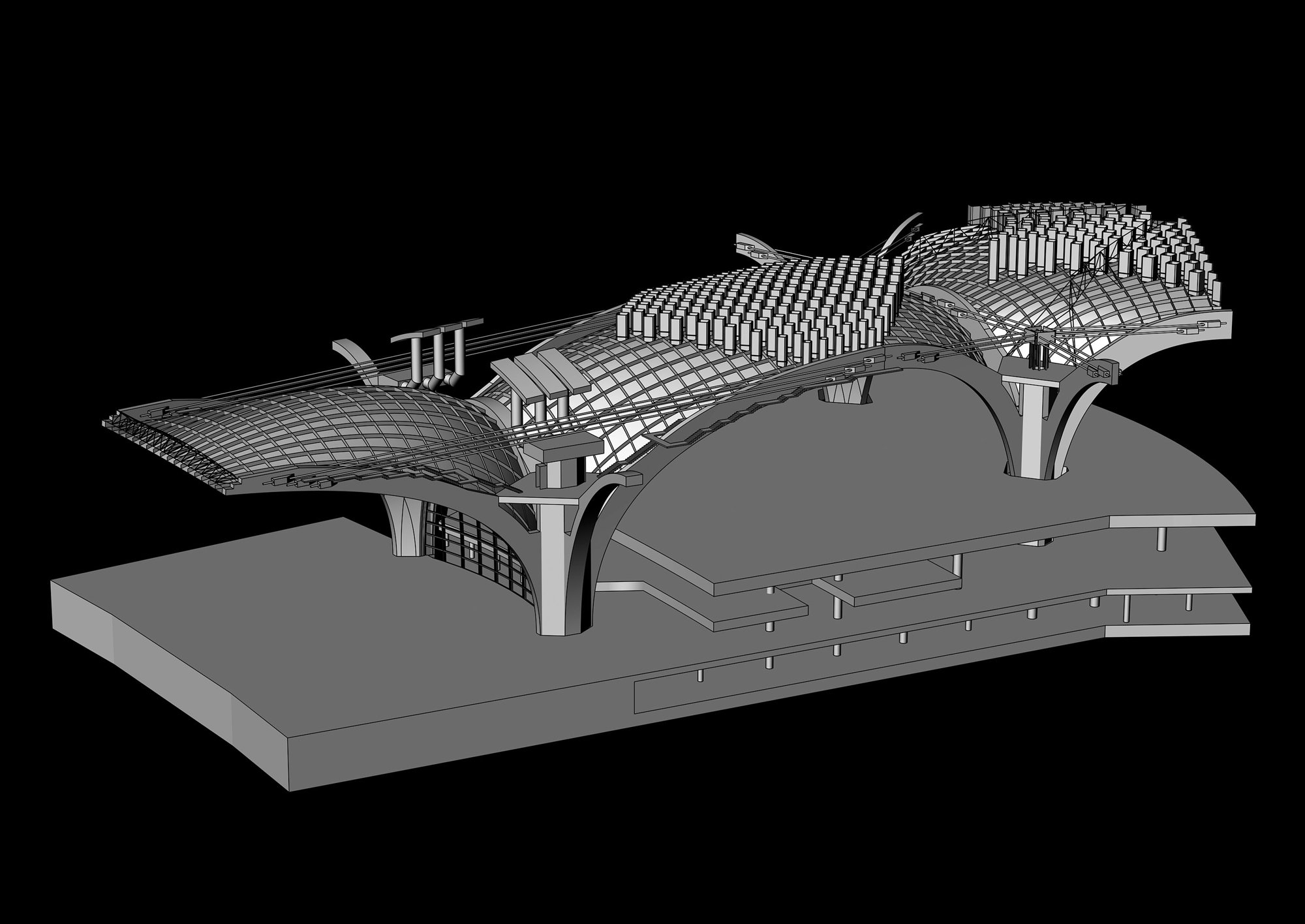
The terminal has a trefoil plan, comprising three symmetrical wings of departure gates. Each façade spans 1.2 kilometres and all extend from a dramatic 25-metre-high central space. The terminal balances the enclosure of this vast area with a design that is highly legible at a human scale - for simplicity and ease of use there are few level changes. To further aid orientation, the building is planned under a single roof canopy, punctuated by glazed openings that filter daylight, while deflecting direct solar radiation. The canopy extends to shade a generous entrance plaza and is supported by tapering concrete columns - their fluid, organic forms draw inspiration from the contrast between the solidity of the stone and the shape and movement of Kuwait's traditional dhow sailing boats. Targeting LEED 'gold', it aims to be the first passenger terminal in the world to attain this level of environmental accreditation and combines the thermal properties of the concrete structure with a large expanse of roof-mounted photovoltaic panels to harvest solar energy.
Drawing on the region's culture of hospitality and welcoming guests to Kuwait, the design establishes an elegant and memorable arrival sequence for passengers, which includes a baggage reclaim area surrounded by cooling cascades of water. The design also features a grand new landside access sequence from the south. Close to the building, the landscaping is a lush oasis, with strands of drier planting and species native to the desert climate extending further away from the terminal.